Know Your Hardiness Zone in USA in 2024
Whether you’re planting vegetables, flowers, shrubs, or trees, knowing your USDA Hardiness Zone is crucial for making informed decisions about what will thrive in your garden. Hardiness zones, also known as planting or growing zones,are an important tool for gardeners across the U.S., helping you select plants that are best suited for your climate. Here’s why understanding your zone is essential and how to use it effectively for better gardening success.
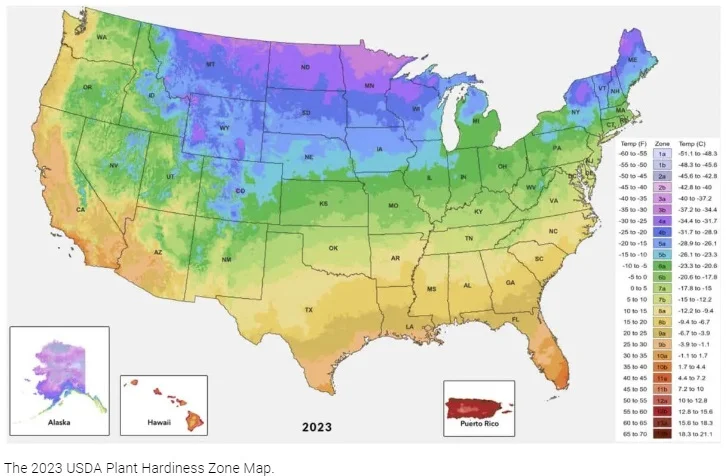
What Are Hardiness Zones?
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) developed the hardiness zone map to divide North America into 13 zones based on the average minimum winter temperatures. Each zone represents a 10°F range, with lower numbers indicating colder regions and higher numbers reflecting warmer areas.
For example:
- Zone 3 has average winter lows of -30 to -40°F, making it one of the coldest zones.
- Zone 9 has winter lows between 20 and 30°F, common in southern parts of the U.S. like Florida and Texas.
Why Is Knowing Your Zone Important?
Understanding your hardiness zone allows you to choose plants that can survive the winter in your area. When you pick plants that are outside of your zone, you risk them not surviving the cold (or heat) of the seasons. By selecting plants rated for your zone or lower, you increase your chances of long-term gardening success.
For instance, if you live in Zone 6 and buy a plant rated for Zone 9, it’s likely that your plant won’t survive the winter chill. Conversely, a plant that thrives in Zone 4 would do just fine in your Zone 6 garden since it’s adapted to even colder temperatures.
How to Find Your Hardiness Zone
Finding your hardiness zone is easy! Simply use the USDA’s interactive hardiness zone map online. By entering your zip code, you can quickly discover which zone you are in. This will help you make better choices when purchasing plants from nurseries or seed catalogs, many of which label plants with their hardiness zones.

Adjusting Your Gardening Practices
While your hardiness zone provides a solid guideline, microclimates, elevation, and local weather patterns can also affect what grows best in your yard. For instance, urban areas tend to have slightly warmer microclimates than surrounding rural areas. If your garden is in a more sheltered location or near a south-facing wall, you might be able to grow plants that are on the edge of your zone.

In addition, while hardiness zones focus on cold tolerance, other factors like humidity, rainfall, and soil type are also important. Keep these in mind as you plan your garden.
Choosing Plants for Your Zone
Most plant labels and online catalogs will provide the USDA hardiness zone range. Choose plants within your zone or lower to ensure they’ll handle your winter temperatures. You can also explore plants native to your region—they are already adapted to the local climate and often need less care.

For example:
- Zone 5-7: Daylilies, coneflowers, and hostas are popular perennials that thrive in these cooler regions.
- Zone 8-10: Warm-climate plants like bougainvillea, oleander, and citrus trees flourish in the hotter zones.
Hardiness Zones and Annuals
While perennial plants are heavily influenced by hardiness zones, annuals can be more flexible since they complete their life cycle in one growing season. You can grow many annuals, like tomatoes or zinnias, even in zones where they wouldn’t survive the winter, as long as they are planted after the danger of frost has passed.
Plan for Success
Knowing your hardiness zone is the first step toward creating a thriving, sustainable garden. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned gardener, selecting the right plants for your climate will save you time, money, and frustration. So, before you make your next plant purchase, be sure to check the hardiness zone, and let your garden grow with confidence!

By tailoring your garden to your zone, you ensure that your plants will be hardy and strong, weathering the challenges of each season with ease.
Happy gardening!

Leave a Reply